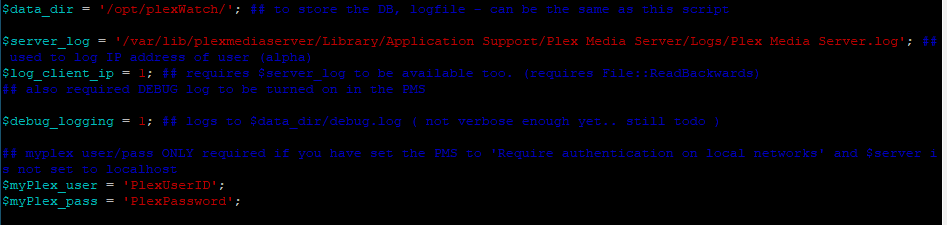
I have been helping a company move to a new cloud based email system. They needed to update everyone’s mail profile. In this follow VBScript, it builds a .prf file to be imported in with the correct fields for the user and servers. Near the top of the script there is a section to be filled out by a person that knows the Exchange environment, Exchange Administrator.
The script will ask the user their primary email address. For the company I was helping out they had multiple email domains so we needed them to select their primary. It then will ask them to confirm what they typed.
‘++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
‘ Add email profile for Another Exchange Provider
‘++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Option Explicit
On Error Resume Next’ Declare our varibles
Dim template, strInput, intAnswer, strProxy, strAutoDiscoverProxy, strProfileName, strHomeServer, strRPCProxyPrincipalName’ Define our servers and paths Examples
strProxy = “” ‘ strProxy = “webmail.yourdomain.com”
strAutoDiscoverProxy = “” ‘ strAutoDiscoverProxy = “https://webmail.yourdomain.com/autodiscoverproxy/autodiscover.xml”
strProfileName = “” ‘ strProfileName = “New Cloud Email”
strHomeServer = “” ‘ strHomeServer = “MyExchangeServer”
strRPCProxyPrincipalName = “” ‘ strRPCProxyPrincipalName = “msstd:webmail.yourdomain.com”‘ This loop section is here to have the user verify their email address
‘ Starting the Loop. This will loop from this point until the answer is Yes
Do Until intAnswer = vbYes‘ Asking the user their primary email address
strInput = UserInput( “Please enter your primary email address:” )
‘ This is asking the user to confirm their primary email address
intAnswer = _
Msgbox(“Completing reconfiguration of Outlook for email address: ” & strInput & vbCr & “This is correct?”, _
vbYesNo, “Confirm Email Address”)
‘ This will loop the script back to the start of the Loop function. If the user click
‘ Yes, then the function will exit the loop. If the user answered No, the function will
‘ start over and prompt the user for their primary email address.
Loop
Function UserInput( myPrompt )
‘ This function prompts the user for some input.
‘ When the script runs in CSCRIPT.EXE, StdIn is used,
‘ otherwise the VBScript InputBox( ) function is used.
‘ myPrompt is the the text used to prompt the user for input.
‘ The function returns the input typed either on StdIn or in InputBox( ).
‘ Written by Rob van der Woude
‘ http://www.robvanderwoude.com
‘ Check if the script runs in CSCRIPT.EXE
If UCase( Right( WScript.FullName, 12 ) ) = “\CSCRIPT.EXE” Then
‘ If so, use StdIn and StdOut
WScript.StdOut.Write myPrompt & ” “
UserInput = WScript.StdIn.ReadLine
Else
‘ If not, use InputBox( )
UserInput = InputBox( myPrompt )
End If
End Function
template = “;Automatically generated PRF file” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“; **************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 1 – Profile Defaults” & VbCrLF &_
“; **************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[General]” & VbCrLF &_
“Custom=1” & VbCrLF &_
“ProfileName=Cloud Email” & VbCrLF &_
“DefaultProfile=No” & VbCrLF &_
“OverwriteProfile=No” & VbCrLF &_
“ModifyDefaultProfileIfPresent=FALSE” & VbCrLF &_
“BackupProfile=No ” & VbCrLF &_
“DefaultStore=Service1” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“; **************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 2 – Services in Profile” & VbCrLF &_
“; **************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Service List]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceX=Microsoft Outlook Client” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceEGS=Exchange Global Section” & VbCrLF &_
“Service1=Microsoft Exchange Server” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceEGS=Exchange Global Section” & VbCrLF &_
“Service2=Outlook Address Book” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 3 – List of internet accounts” & VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Internet Account List]” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 4 – Default values for each service.” & VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[ServiceX]” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeMode=0x00000002” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeSlowDetect=TRUE” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[ServiceEGS]” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeConfigFlags=0x00000100” & VbCrLF &_
“MailboxName=” & strInput & VbCrLF &_
“HomeServer=” & strHomeServer & VbCrLF &_
“RPCoverHTTPflags=0x002f” & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyServer=” & strProxy & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyPrincipalName=msstd:” & strRPCProxyPrincipalName & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyAuthScheme=0x0001” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Service1]” & VbCrLF &_
“OverwriteExistingService=No” & VbCrLF &_
“UniqueService=No” & VbCrLF &_
“MailboxName=” & strInput & VbCrLF &_
“HomeServer=” & strHomeServer & VbCrLF &_
“AccountName=Microsoft Exchange Server” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 5 – Values for each internet account.” & VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 6 – Mapping for profile properties” & VbCrLF &_
“;***************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Microsoft Exchange Server]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=MSEMS” & VbCrLF &_
“MDBGUID=5494A1C0297F101BA58708002B2A2517” & VbCrLF &_
“MailboxName=PT_STRING8,0x6607” & VbCrLF &_
“HomeServer=PT_STRING8,0x6608” & VbCrLF &_
“OfflineAddressBookPath=PT_STRING8,0x660E” & VbCrLF &_
“OfflineFolderPath=PT_STRING8,0x6610” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Exchange Global Section]” & VbCrLF &_
“SectionGUID=13dbb0c8aa05101a9bb000aa002fc45a” & VbCrLF &_
“MailboxName=PT_STRING8,0x6607” & VbCrLF &_
“HomeServer=PT_STRING8,0x6608” & VbCrLF &_
“RPCoverHTTPflags=PT_LONG,0x6623” & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyServer=PT_UNICODE,0x6622” & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyPrincipalName=PT_UNICODE,0x6625” & VbCrLF &_
“RPCProxyAuthScheme=PT_LONG,0x6627” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeConfigFlags=PT_LONG,0x6629” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Microsoft Mail]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=MSFS” & VbCrLF &_
“ServerPath=PT_STRING8,0x6600” & VbCrLF &_
“Mailbox=PT_STRING8,0x6601” & VbCrLF &_
“Password=PT_STRING8,0x67f0” & VbCrLF &_
“RememberPassword=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6606” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionType=PT_LONG,0x6603” & VbCrLF &_
“UseSessionLog=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6604” & VbCrLF &_
“SessionLogPath=PT_STRING8,0x6605” & VbCrLF &_
“EnableUpload=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6620” & VbCrLF &_
“EnableDownload=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6621” & VbCrLF &_
“UploadMask=PT_LONG,0x6622” & VbCrLF &_
“NetBiosNotification=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6623” & VbCrLF &_
“NewMailPollInterval=PT_STRING8,0x6624” & VbCrLF &_
“DisplayGalOnly=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6625” & VbCrLF &_
“UseHeadersOnLAN=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6630” & VbCrLF &_
“UseLocalAdressBookOnLAN=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6631” & VbCrLF &_
“UseExternalToHelpDeliverOnLAN=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6632” & VbCrLF &_
“UseHeadersOnRAS=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6640” & VbCrLF &_
“UseLocalAdressBookOnRAS=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6641” & VbCrLF &_
“UseExternalToHelpDeliverOnRAS=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6639” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectOnStartup=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6642” & VbCrLF &_
“DisconnectAfterRetrieveHeaders=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6643” & VbCrLF &_
“DisconnectAfterRetrieveMail=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6644” & VbCrLF &_
“DisconnectOnExit=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6645” & VbCrLF &_
“DefaultDialupConnectionName=PT_STRING8,0x6646” & VbCrLF &_
“DialupRetryCount=PT_STRING8,0x6648” & VbCrLF &_
“DialupRetryDelay=PT_STRING8,0x6649” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Personal Folders]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=MSPST MS” & VbCrLF &_
“Name=PT_STRING8,0x3001” & VbCrLF &_
“PathToPersonalFolders=PT_STRING8,0x6700 ” & VbCrLF &_
“RememberPassword=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6701” & VbCrLF &_
“EncryptionType=PT_LONG,0x6702” & VbCrLF &_
“Password=PT_STRING8,0x6703” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Unicode Personal Folders]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=MSUPST MS” & VbCrLF &_
“Name=PT_UNICODE,0x3001” & VbCrLF &_
“PathToPersonalFolders=PT_STRING8,0x6700 ” & VbCrLF &_
“RememberPassword=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6701” & VbCrLF &_
“EncryptionType=PT_LONG,0x6702” & VbCrLF &_
“Password=PT_STRING8,0x6703” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Outlook Address Book]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=CONTAB” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[LDAP Directory]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=EMABLT” & VbCrLF &_
“ServerName=PT_STRING8,0x6600” & VbCrLF &_
“UserName=PT_STRING8,0x6602” & VbCrLF &_
“UseSSL=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6613” & VbCrLF &_
“UseSPA=PT_BOOLEAN,0x6615” & VbCrLF &_
“DisableVLV=PT_LONG,0x6616” & VbCrLF &_
“DisplayName=PT_STRING8,0x3001” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionPort=PT_STRING8,0x6601” & VbCrLF &_
“SearchTimeout=PT_STRING8,0x6607” & VbCrLF &_
“MaxEntriesReturned=PT_STRING8,0x6608” & VbCrLF &_
“SearchBase=PT_STRING8,0x6603” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Microsoft Outlook Client]” & VbCrLF &_
“SectionGUID=0a0d020000000000c000000000000046” & VbCrLF &_
“FormDirectoryPage=PT_STRING8,0x0270” & VbCrLF &_
“WebServicesLocation=PT_STRING8,0x0271” & VbCrLF &_
“ComposeWithWebServices=PT_BOOLEAN,0x0272” & VbCrLF &_
“PromptWhenUsingWebServices=PT_BOOLEAN,0x0273” & VbCrLF &_
“OpenWithWebServices=PT_BOOLEAN,0x0274” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeMode=PT_LONG,0x041f” & VbCrLF &_
“CachedExchangeSlowDetect=PT_BOOLEAN,0x0420” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[Personal Address Book]” & VbCrLF &_
“ServiceName=MSPST AB” & VbCrLF &_
“NameOfPAB=PT_STRING8,0x001e3001” & VbCrLF &_
“Path=PT_STRING8,0x001e6600” & VbCrLF &_
“ShowNamesBy=PT_LONG,0x00036601” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“; ************************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
“; Section 7 – Mapping for internet account properties. DO NOT MODIFY.” & VbCrLF &_
“; ************************************************************************” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[I_Mail]” & VbCrLF &_
“AccountType=POP3” & VbCrLF &_
“;— POP3 Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“AccountName=PT_UNICODE,0x0002” & VbCrLF &_
“DisplayName=PT_UNICODE,0x000B” & VbCrLF &_
“EmailAddress=PT_UNICODE,0x000C” & VbCrLF &_
“;— POP3 Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“POP3Server=PT_UNICODE,0x0100” & VbCrLF &_
“POP3UserName=PT_UNICODE,0x0101” & VbCrLF &_
“POP3UseSPA=PT_LONG,0x0108” & VbCrLF &_
“Organization=PT_UNICODE,0x0107” & VbCrLF &_
“ReplyEmailAddress=PT_UNICODE,0x0103” & VbCrLF &_
“POP3Port=PT_LONG,0x0104” & VbCrLF &_
“POP3UseSSL=PT_LONG,0x0105” & VbCrLF &_
“; — SMTP Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPServer=PT_UNICODE,0x0200” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseAuth=PT_LONG,0x0203” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPAuthMethod=PT_LONG,0x0208” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUserName=PT_UNICODE,0x0204” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseSPA=PT_LONG,0x0207” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionType=PT_LONG,0x000F” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionOID=PT_UNICODE,0x0010” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPPort=PT_LONG,0x0201” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseSSL=PT_LONG,0x0202” & VbCrLF &_
“ServerTimeOut=PT_LONG,0x0209” & VbCrLF &_
“LeaveOnServer=PT_LONG,0x1000” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[IMAP_I_Mail]” & VbCrLF &_
“AccountType=IMAP” & VbCrLF &_
“;— IMAP Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“AccountName=PT_UNICODE,0x0002” & VbCrLF &_
“DisplayName=PT_UNICODE,0x000B” & VbCrLF &_
“EmailAddress=PT_UNICODE,0x000C” & VbCrLF &_
“;— IMAP Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“IMAPServer=PT_UNICODE,0x0100” & VbCrLF &_
“IMAPUserName=PT_UNICODE,0x0101” & VbCrLF &_
“IMAPUseSPA=PT_LONG,0x0108” & VbCrLF &_
“Organization=PT_UNICODE,0x0107” & VbCrLF &_
“ReplyEmailAddress=PT_UNICODE,0x0103” & VbCrLF &_
“IMAPPort=PT_LONG,0x0104” & VbCrLF &_
“IMAPUseSSL=PT_LONG,0x0105” & VbCrLF &_
“; — SMTP Account Settings —” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPServer=PT_UNICODE,0x0200” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseAuth=PT_LONG,0x0203” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPAuthMethod=PT_LONG,0x0208” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUserName=PT_UNICODE,0x0204” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseSPA=PT_LONG,0x0207” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionType=PT_LONG,0x000F” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectionOID=PT_UNICODE,0x0010” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPPort=PT_LONG,0x0201” & VbCrLF &_
“SMTPUseSSL=PT_LONG,0x0202” & VbCrLF &_
“ServerTimeOut=PT_LONG,0x0209” & VbCrLF &_
“CheckNewImap=PT_LONG,0x1100” & VbCrLF &_
“RootFolder=PT_UNICODE,0x1101” & VbCrLF &_
VbCrLF &_
“[INET_HTTP]” & VbCrLF &_
“AccountType=HOTMAIL” & VbCrLF &_
“Account=PT_UNICODE,0x0002” & VbCrLF &_
“HttpServer=PT_UNICODE,0x0100” & VbCrLF &_
“UserName=PT_UNICODE,0x0101” & VbCrLF &_
“Organization=PT_UNICODE,0x0107” & VbCrLF &_
“UseSPA=PT_LONG,0x0108” & VbCrLF &_
“TimeOut=PT_LONG,0x0209” & VbCrLF &_
“Reply=PT_UNICODE,0x0103” & VbCrLF &_
“EmailAddress=PT_UNICODE,0x000C” & VbCrLF &_
“FullName=PT_UNICODE,0x000B” & VbCrLF &_
“Connection Type=PT_LONG,0x000F” & VbCrLF &_
“ConnectOID=PT_UNICODE,0x0010” & VbCrLF
Dim objShell, fso
Set objShell = WScript.CreateObject(“WScript.Shell”)
Set fso = CreateObject(“Scripting.FileSystemObject”)
‘Check for valid windows version
If Not CheckWindowsVersion Then
ExitWithError(“UnsupportedVersion”)
End If
‘Get Outlook Path
Dim outlookPath
outlookPath = GetOutlookPath
If outlookPath = “” Then
ExitWithError(“OutlookNotFound”)
End If
‘Check that Outlook does not running
Dim answer
Do While True
If CheckOutlookIsRunning Then
answer = MsgBox(GetString(“OutlookIsRunning”), vbRetryCancel ,GetString (“MessageCaption”))
If answer = vbCancel Then
WScript.Quit
End If
Else
Exit Do
End If
Loop
‘Adjust Outlook registry settings
AdjustSettings
‘ Configure Autodiscover for Custom email address
Dim customEmail
customEmail = “”
If customEmail <> “” Then
ConfigureAutodiscover customEmail
End If
‘Create temporary file for Outlook profile
Dim tempFile, tempFileName
tempFileName = GetTempFileName
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
ExitWithError(“ProfileCreateError”)
End If
Set tempFile = fso.CreateTextFile(tempFileName, true, true)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
ExitWithError(“ProfileCreateError”)
End If
‘Write profile to file
tempFile.Write(template)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
ExitWithError(“ProfileWriteError”)
End If
tempFile.Close
‘Start Outlook
objShell.Exec(outlookPath + ” /importprf “”” + tempFileName + “”””)
Function CheckWindowsVersion
On Error Resume Next
Dim objWMI, colOS, objOS, version
set objWMI = GetObject(“winmgmts:\\.\root\cimv2”)
set colOS = objWMI.InstancesOf(“Win32_OperatingSystem”)
For Each objOS in colOS
version = objOS.Version
If objOS.OSType = 18 Then
If Left(version, 1) > 5 Then
‘ Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
ElseIf Left(version, 1) = 5 And Mid(version, 3, 1) = 2 Then
If objOS.OtherTypeDescription = “R2” Then
‘ Windows Server 2003 R2
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
ElseIf objOS.ProductType = 1 Then
‘ Windows XP Professional x64 Edition
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
Else
‘ Windows Server 2003
If objOS.ServicePackMajorVersion = 0 Then
‘ no any Service Pack
CheckWindowsVersion = False
Exit Function
End If
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
End If
ElseIf Left(version, 1) = 5 And Mid(version, 3, 1) = 1 Then
‘Microsoft Windows XP
If objOS.ServicePackMajorVersion > 1 Then
‘ SP2 or later
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
ElseIf objOS.ServicePackMajorVersion = 1 Then
‘ SP1, check for installed KB331320
Err.Clear
objShell.RegRead(“HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Updates\Windows XP\SP1\KB331320\”)
If Err.Number = 0 Then
CheckWindowsVersion = True
Exit Function
End If
End If
End If
End If
Next
CheckWindowsVersion = False
End Function
Function GetOutlookPath
On Error Resume Next
Dim CLSID, path
‘ First of all check simple location
path = objShell.RegRead(“HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths\OUTLOOK.EXE\”)
If path <> “” Then
GetOutlookPath = path
Exit Function
End If
CLSID = objShell.RegRead(“HKLM\Software\Classes\Outlook.Application\CLSID\”)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
GetOutlookPath “”
Exit Function
End If
path = objShell.RegRead(“HKLM\Software\Classes\CLSID\” & CLSID & “\LocalServer32\”)
‘ Does need to check alternative path ?
if path = “” Then
path = objShell.RegRead(“HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Classes\CLSID\” & CLSID & “\LocalServer32\”)
End If
‘ If we have an error path will be empty
GetOutlookPath = path
End Function
Function CheckOutlookIsRunning
On Error Resume Next
Dim objWMIService, processList
Set objWMIService = GetObject(“winmgmts:\\.\root\cimv2”)
Set processList = objWMIService.ExecQuery(“Select * from Win32_Process Where Name = “”outlook.exe”””)
If processList.Count > 0 Then
CheckOutlookIsRunning = True
Exit Function
End If
CheckOutlookIsRunning = False
End Function
Sub AdjustSettings
objShell.RegWrite “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Exchange\Client\Options\PickLogonProfile”, “1”, “REG_SZ”
End Sub
Function GetTempFileName
Dim tfolder, tname, tfile
Const TemporaryFolder = 2
Set tfolder = fso.GetSpecialFolder(TemporaryFolder)
tname = fso.GetTempName
tfile = fso.BuildPath(tfolder.Path, tname)
GetTempFileName = tfile
End Function
Function ExitWithError(stringId)
MsgBox GetString(stringId), vbOKOnly, GetString(“MessageCaption”)
WScript.Quit
End Function
Function GetString(stringId)
Dim messageCaption, outlookNotFound, outlookIsRunning, profileCreateError, profileWriteError, unsupportedVersion
messageCaption = “Outlook Profile Configuration Script”
outlookNotFound = “Unable to locate Microsoft Outlook installation path.”
outlookIsRunning = “Configuration script has determined that Microsoft Outlook is running. Please shut down it and then click Retry.”
profileCreateError = “Unable to create a temporary file for profile.”
profileWriteError = “Unable to save profile into temporary file.”
unsupportedVersion = “Unsupported version of Microsoft Windows. ” & vbLf & “” & vbLf & “The following versions of Microsoft Windows are supported: ” & vbLf & ” – Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 ” & vbLf & ” – Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 ” & vbLf & ” – or a later operating system”
Dim retStr
Select Case stringId
Case “MessageCaption”
If messageCaption = “” Or Mid(messageCaption, 2, 1) = “4” Then
retStr = “Outlook Profile Configuration Script”
Else
retStr = messageCaption
End If
Case “OutlookNotFound”
If outlookNotFound = “” Or Mid(outlookNotFound, 2, 1) = “5” Then
retStr = “Unable to locate Microsoft Outlook installation path.”
Else
retStr = outlookNotFound
End If
Case “OutlookIsRunning”
If outlookIsRunning = “” Or Mid(outlookIsRunning, 2, 1) = “6” Then
retStr = “Configuration script has determined that Microsoft Outlook is running. Please shut down it and then click Retry.”
Else
retStr = outlookIsRunning
End If
Case “ProfileCreateError”
If profileCreateError = “” Or Mid(profileCreateError, 2, 1) = “7” Then
retStr = “Unable to create a temporary file for profile.”
Else
retStr = profileCreateError
End If
Case “profileWriteError”
If profileWriteError = “” Or Mid(profileWriteError, 2, 1) = “8” Then
retStr = “Unable to save profile into temporary file.”
Else
retStr = profileWriteError
End If
Case “UnsupportedVersion”
If unsupportedVersion = “” Or Mid(unsupportedVersion, 2, 1) = “9” Then
retStr = “Unsupported version of Microsoft Windows. ” & vbLf & “” & vbLf & “The following versions of Microsoft Windows are supported: ” & vbLf & ” – Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 ” & vbLf & ” – Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 ” & vbLf & ” – or a later operating system”
Else
retStr = unsupportedVersion
End If
Case Else
retStr = stringId
End Select
GetString = retStr
End Function
Sub ConfigureAutodiscover(email)
On Error Resume Next
Dim configTemplate
configTemplate = “<?xml version=””1.0″” encoding=””utf-8″”?>” & VbCrLF &_
“<Autodiscover xmlns=””http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/autodiscover/responseschema/2006″”>” & VbCrLF &_
” <Response xmlns=””http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/autodiscover/outlook/responseschema/2006a””>” & VbCrLF &_
” <Account>” & VbCrLF &_
” <AccountType>email</AccountType>” & VbCrLF &_
” <Action>redirectUrl</Action>” & VbCrLF &_
” <RedirectUrl>” & strAutoDiscoverProxy & “</RedirectUrl>” & VbCrLF &_
” </Account>” & VbCrLF &_
” </Response>” & VbCrLF &_
“</Autodiscover>” & VbCrLF
Dim folder
Dim objEnv
‘ Get collection by using the Environment property.
Set objEnv = objShell.Environment(“Process”)
folder = objEnv(“APPDATA”) + “\Outlook\”
‘ Check that Outlook is available
Dim ver
ver = objShell.RegRead(“HKCR\Outlook.Application\CurVer\”)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Outlook.Application.XX -> XX
ver = Right(ver, 2)
Dim mailDomain, configFilePath, configFile
mailDomain = Mid(email, Instr(email, “@”) + 1)
If Not fso.FolderExists(folder) Then
fso.CreateFolder(folder)
End If
configFilePath = folder & mailDomain & “.xml”
Set configFile = fso.CreateTextFile(configFilePath, True)
configFile.Write(configTemplate)
configFile.Close
objShell.RegWrite “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Office\” & ver & “.0\Outlook\AutoDiscover\” & mailDomain, configFilePath, “REG_SZ”
End Sub